This week we have to test runout, alignment, speeds, feeds, and toolpaths for our CNC machine.
What is a CNC machine ?¶
CNC is the short form for Computer Numerical control. In CNC machines the program of instructions is fed directly into the computer via a small board similar to the traditional keyboard you can find on NC machines.
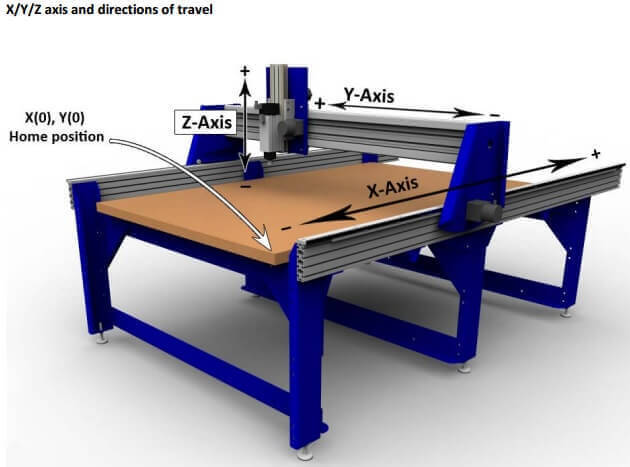
The CNC machine we are using is a Shopbot.

Taking digitized data, a computer and CAM program is used to control, automate, and monitor the movements of the machine.
The CNC controller works together with a series of motors and drive components to move and control the machine axes, executing the programmed motions.
This Shopbot has several axes of movement, and these movements can be either linear or rotary. Milling machines like the one we have usually have at least three, X, Y, and Z, and sometimes can have more rotary axes.
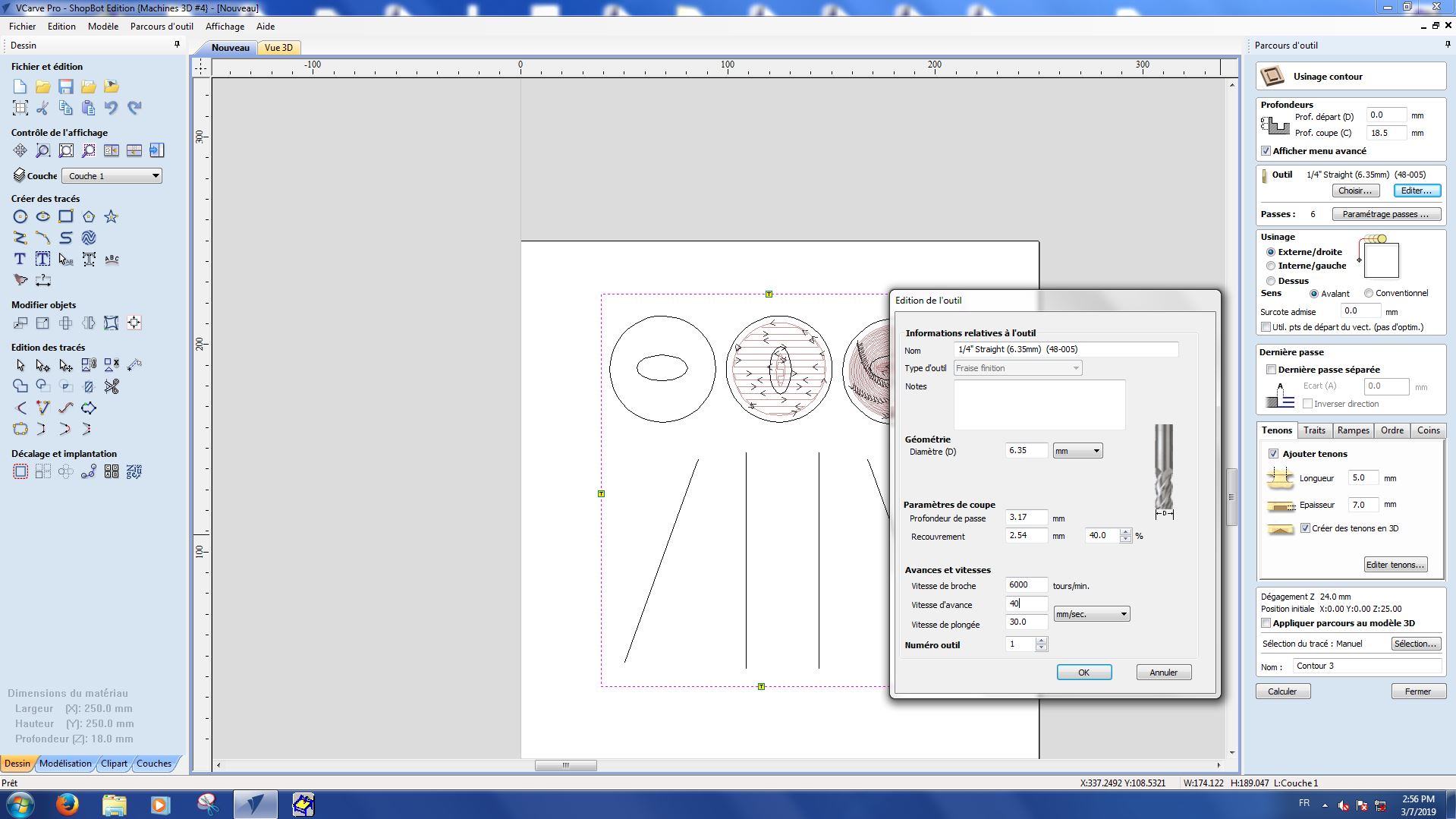
Working with VCarve¶
To control the Shopbot, we have to use the software VCarve. Like Cura for the 3D printer, it translates the coordinates to the machine so it can mill what we want.
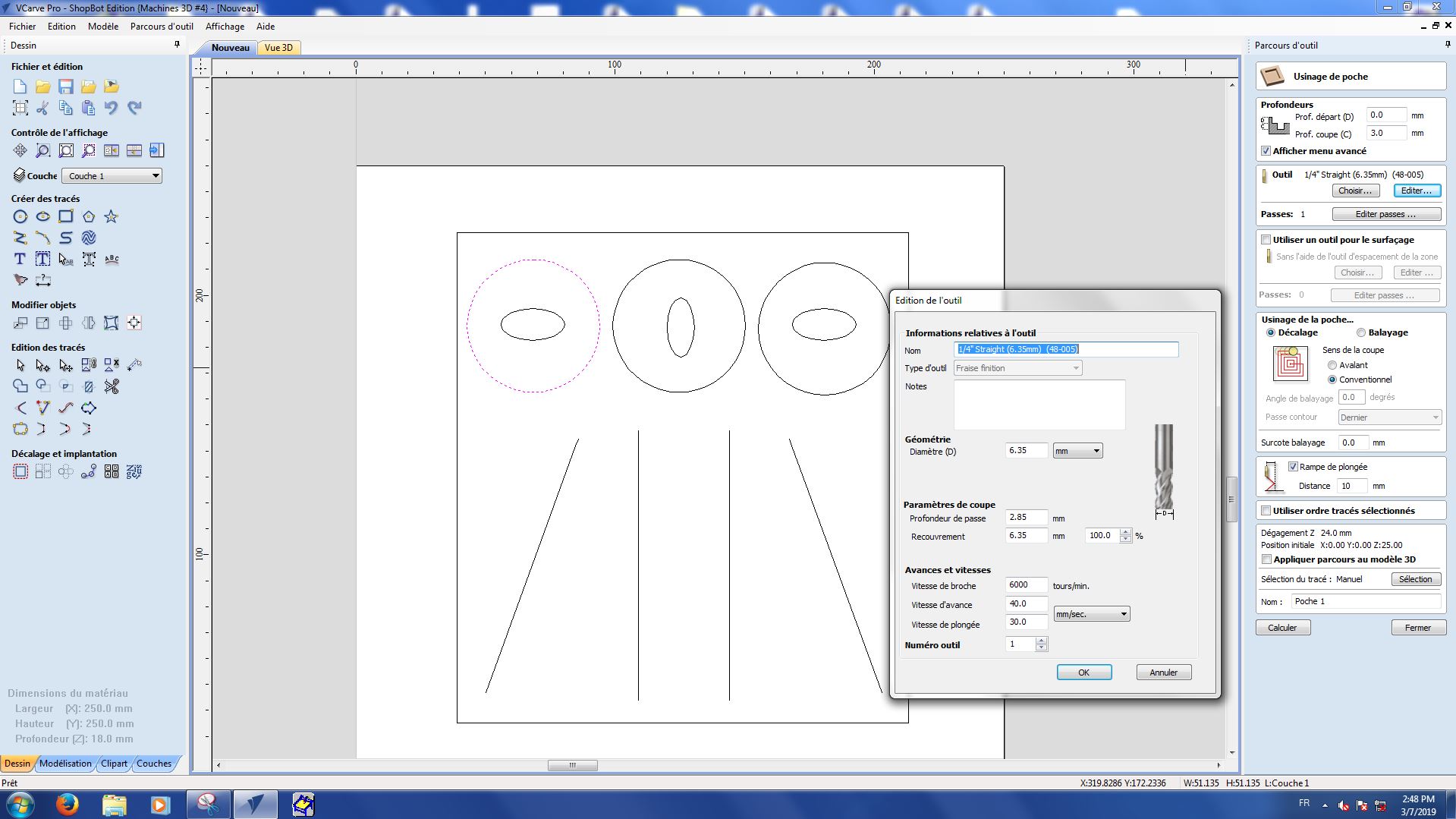
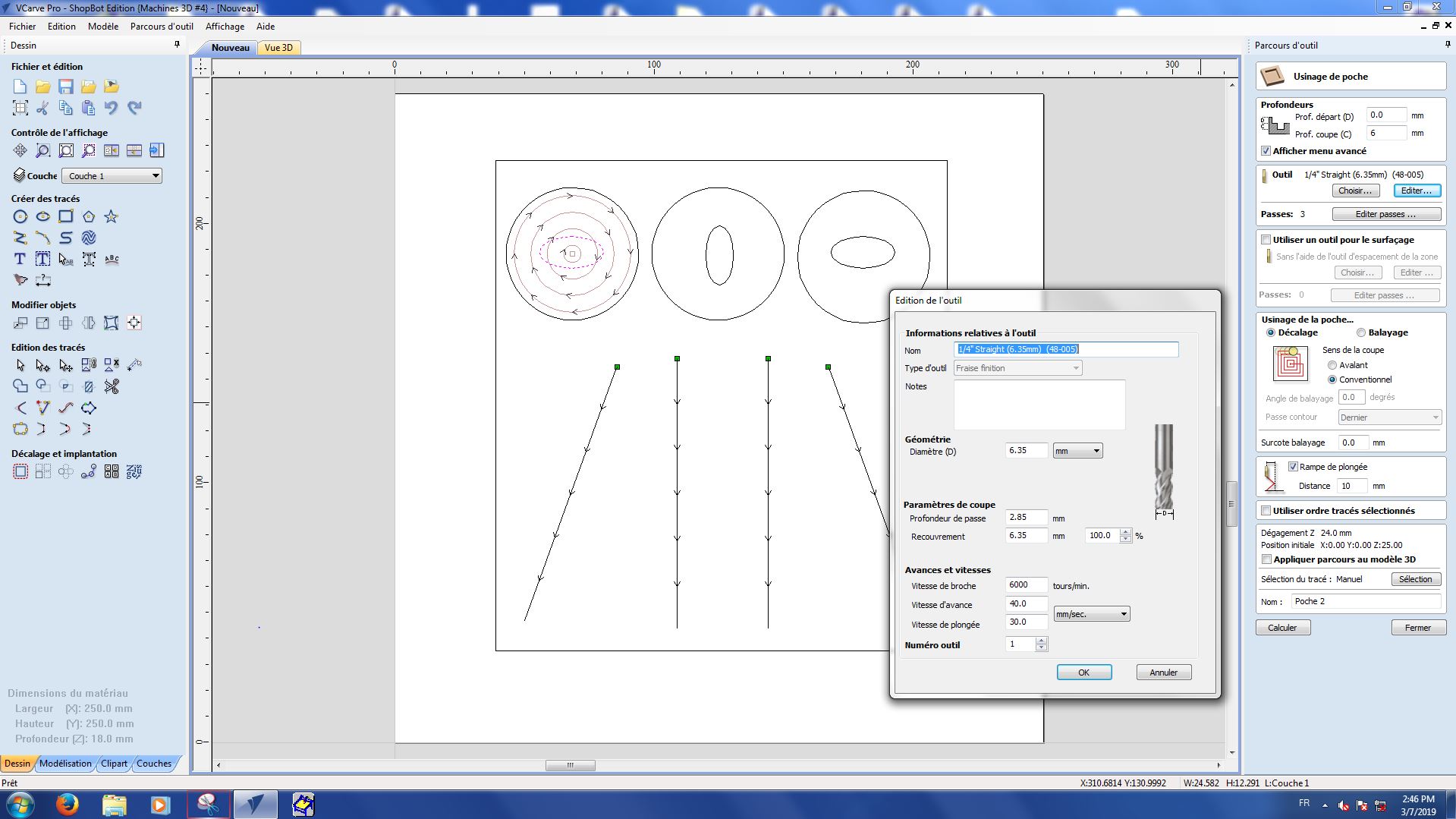
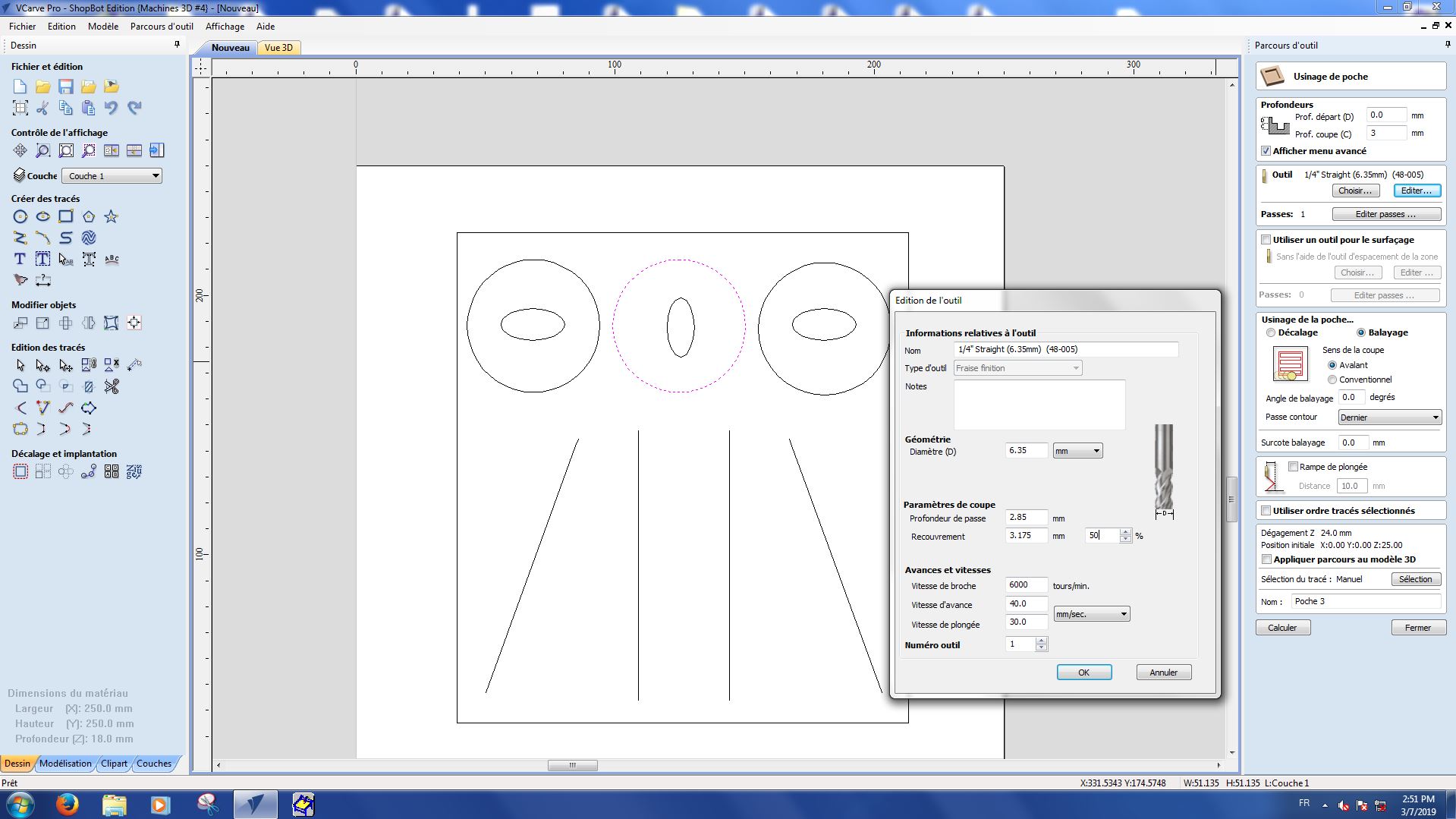
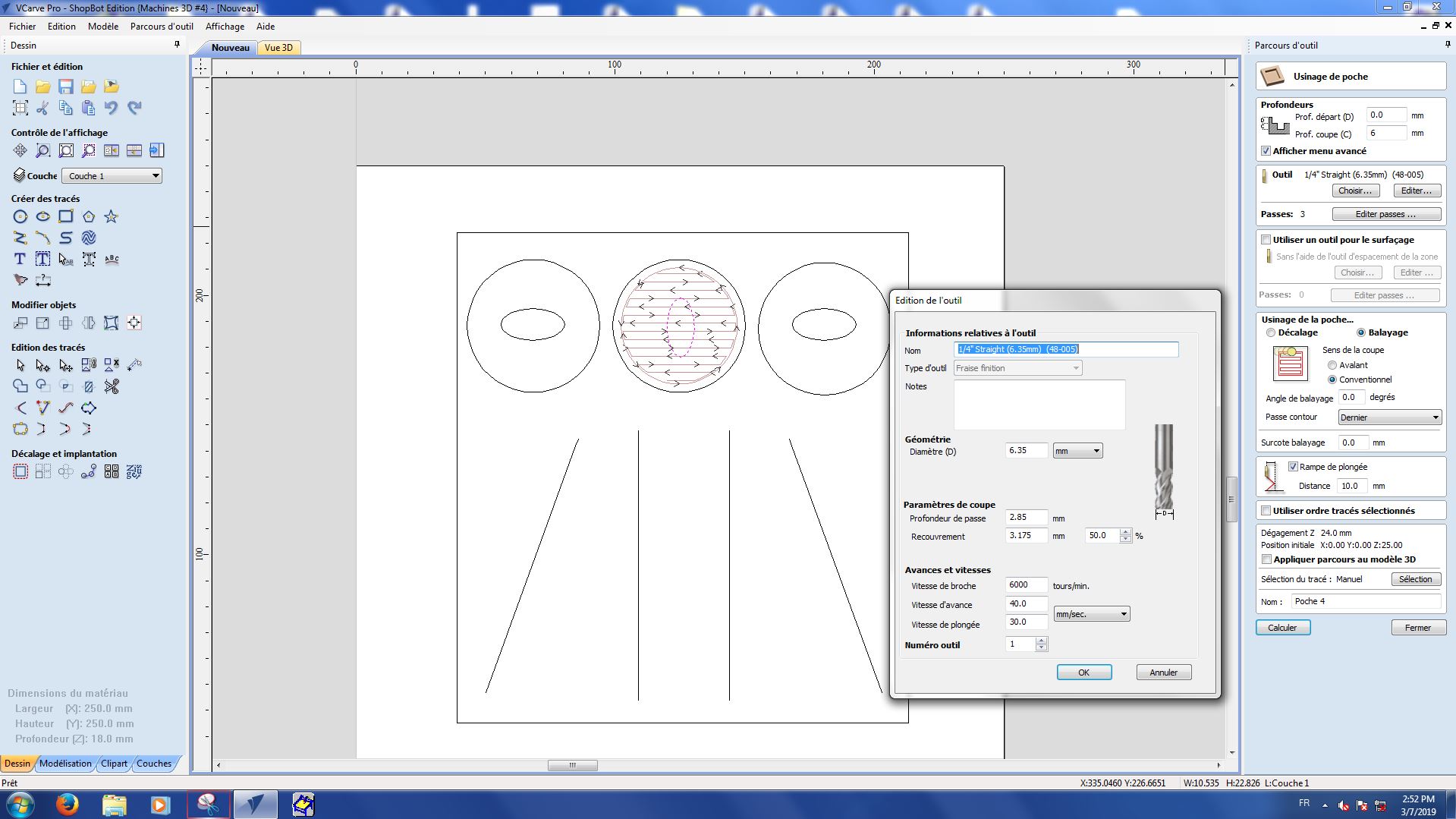
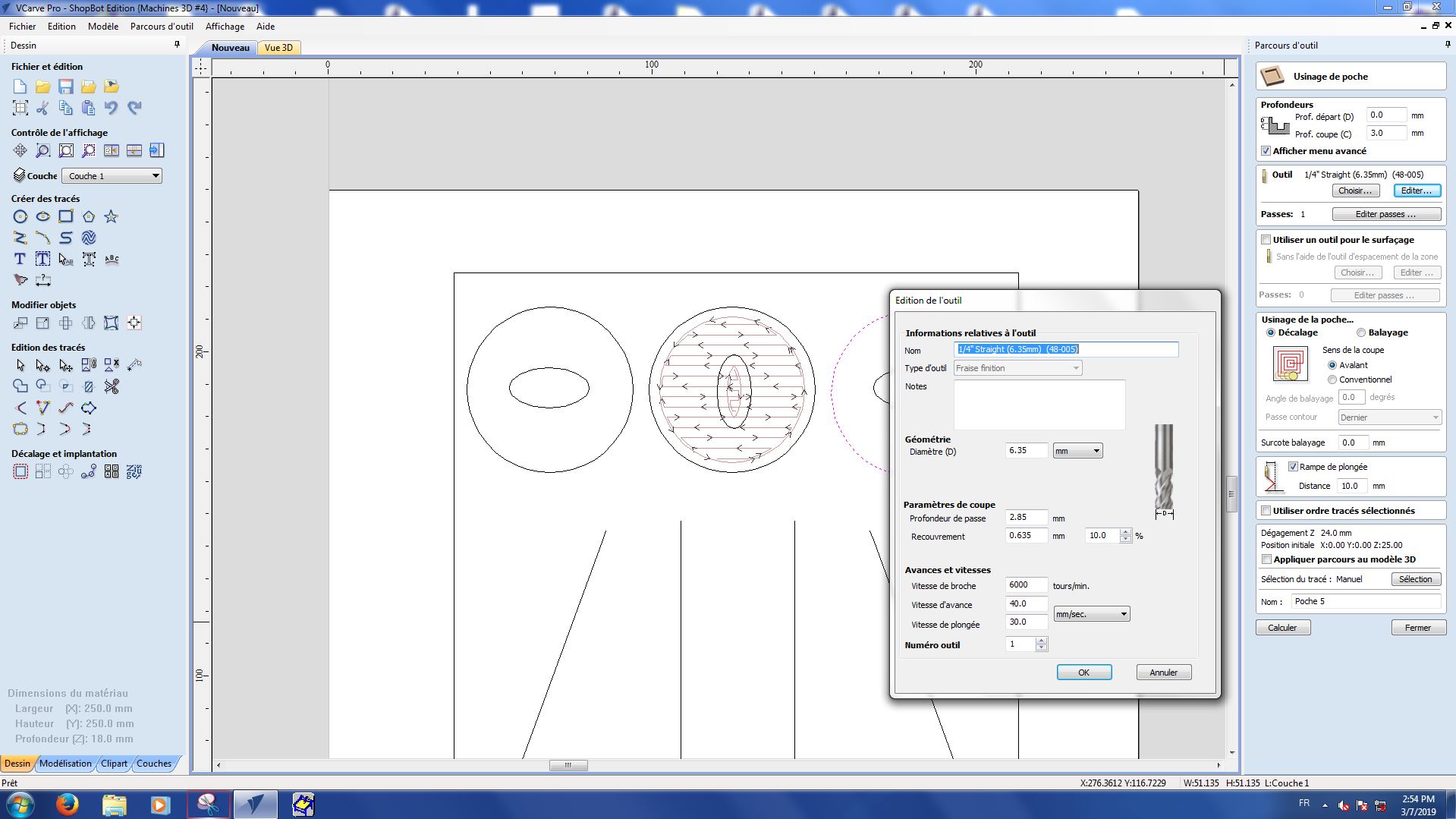
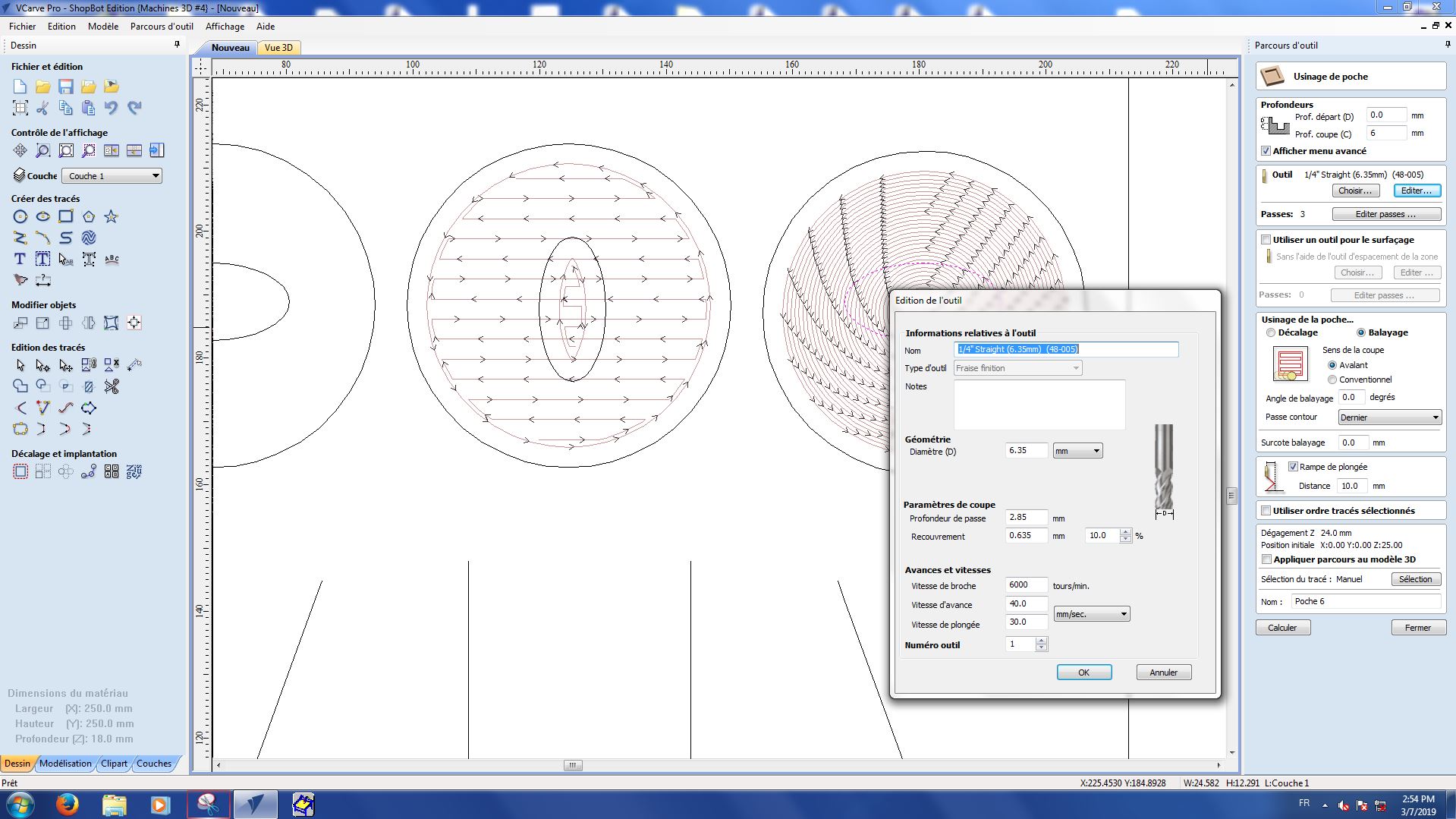
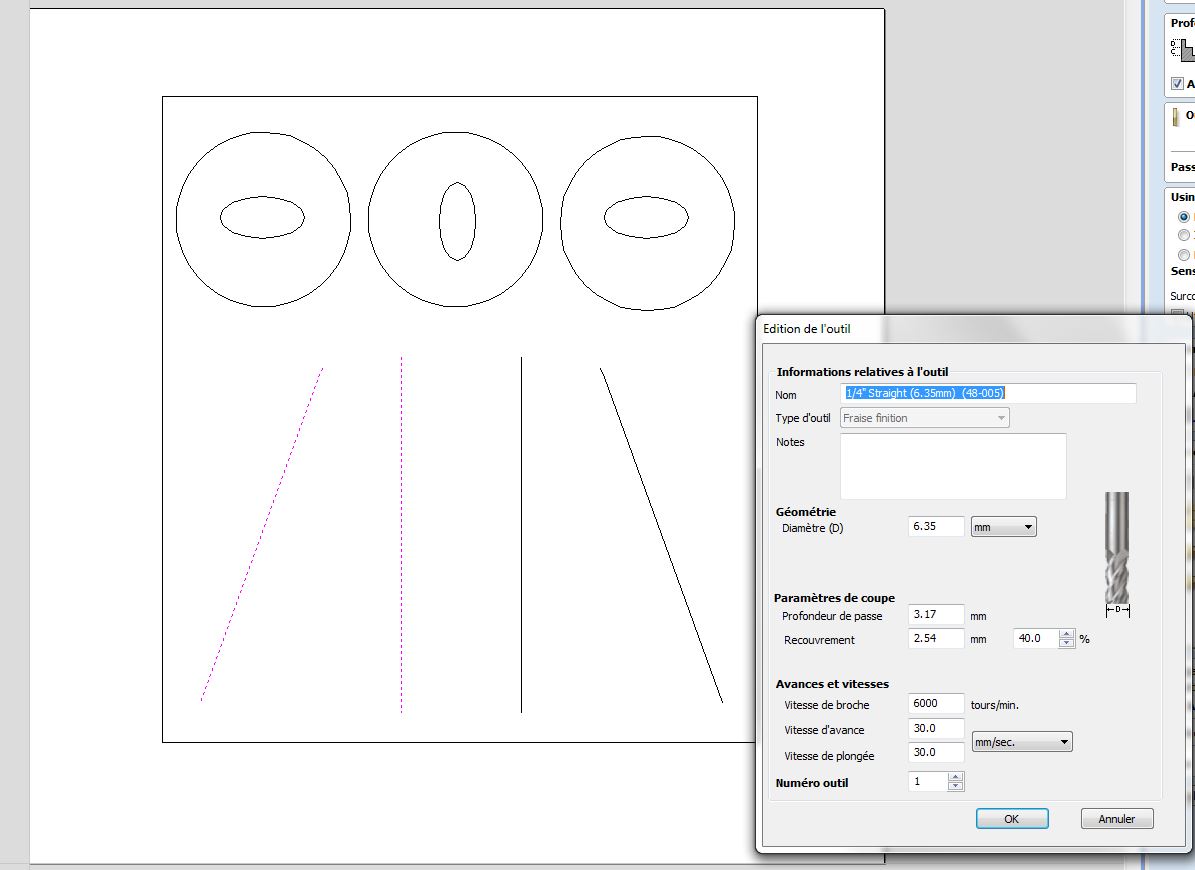
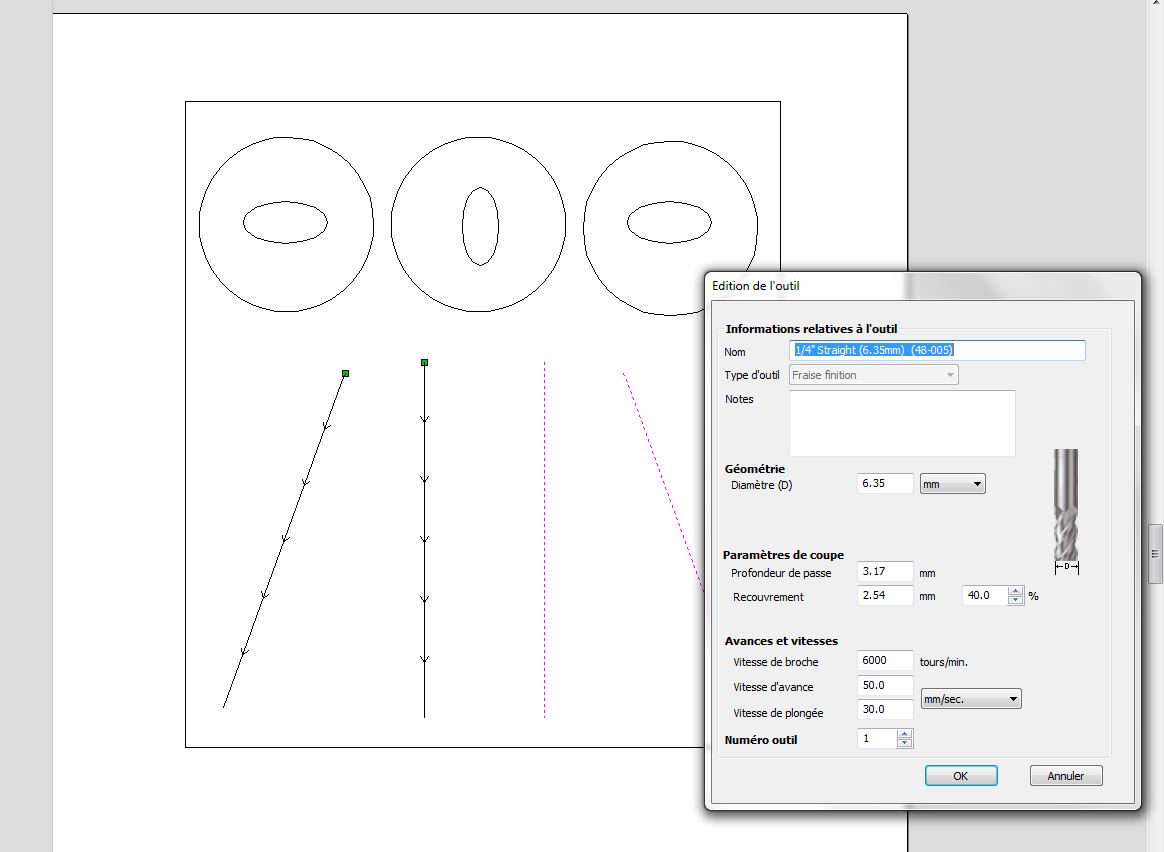
Here are the settings we used for each part :
Step 1 : Pockets
Pocket 1-1
Pocket 1-2
Pocket 2-1
Pocket 2-2
Pocket 3-1
Pocket 3-2
Straight line 1-1
Straight line 1-2
Cutting
Once all the settings are okay, you can launch a simulation of the milling and cutting, to make sure everything goes the way we want.
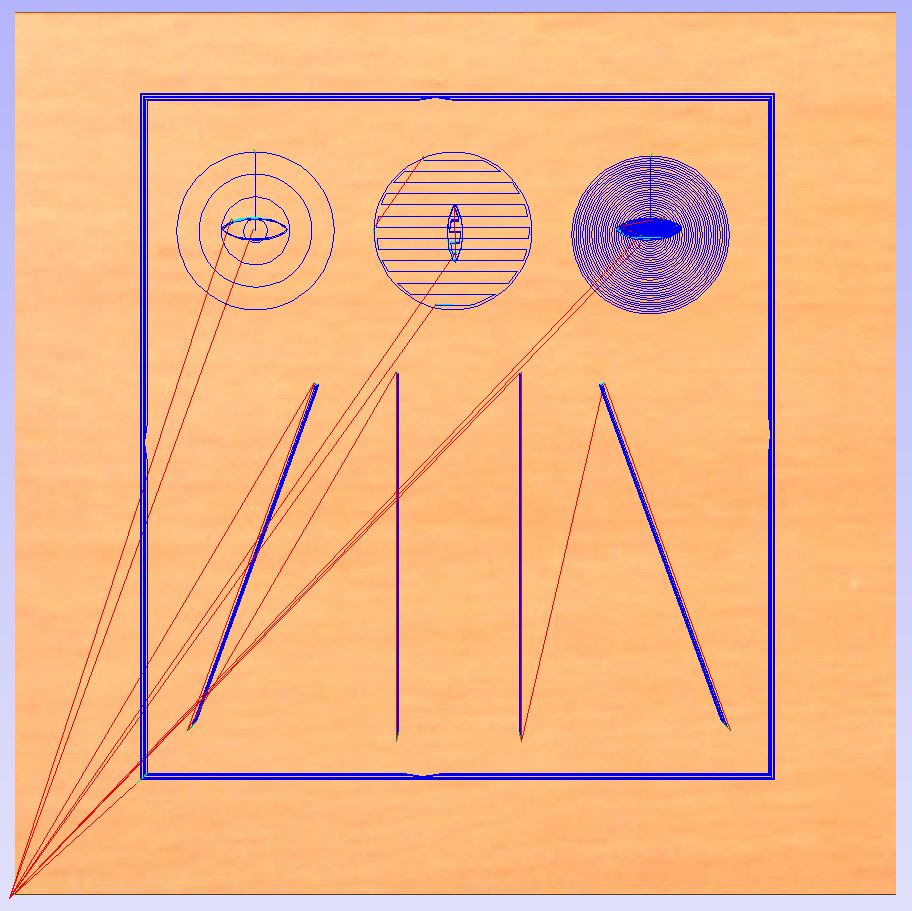
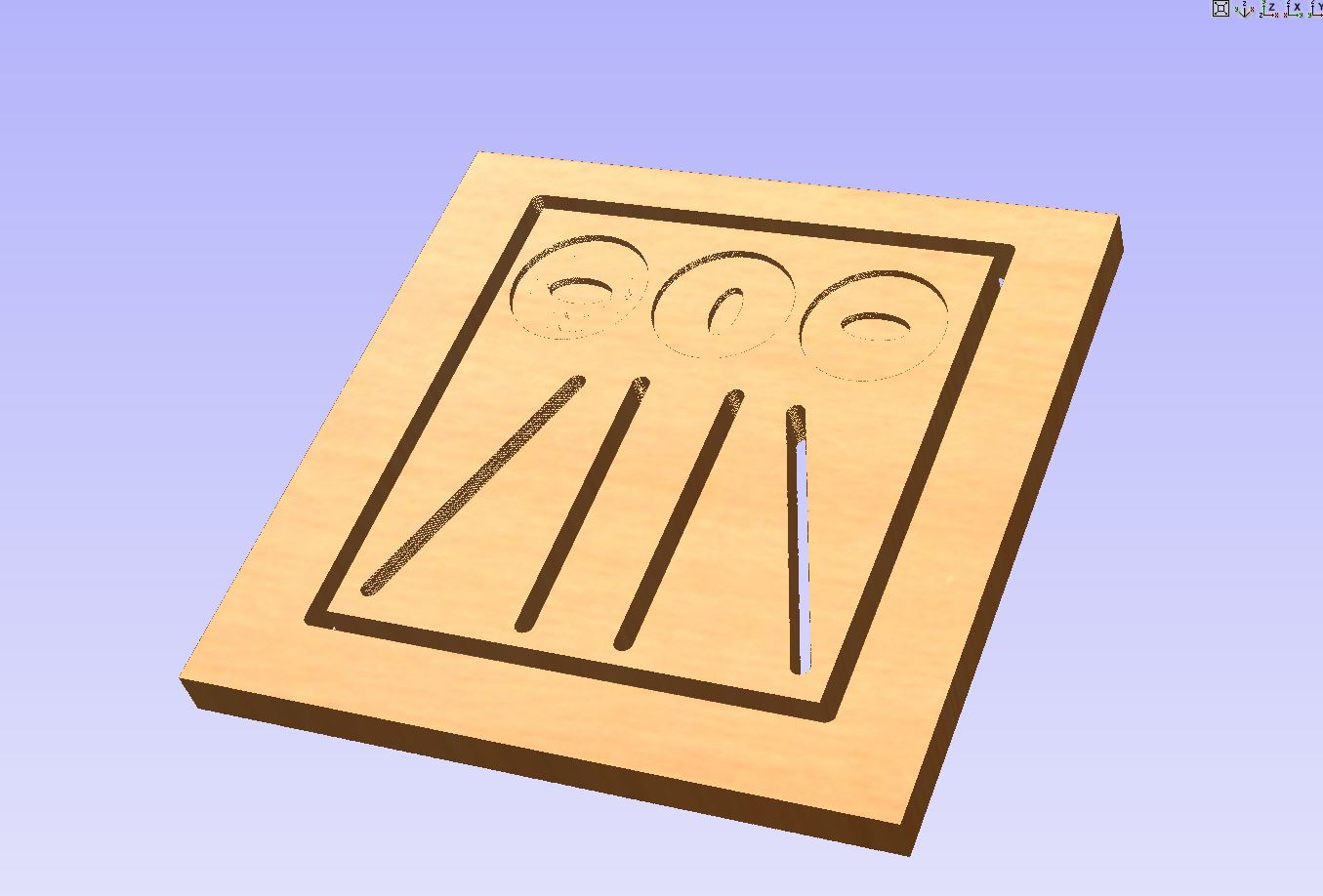
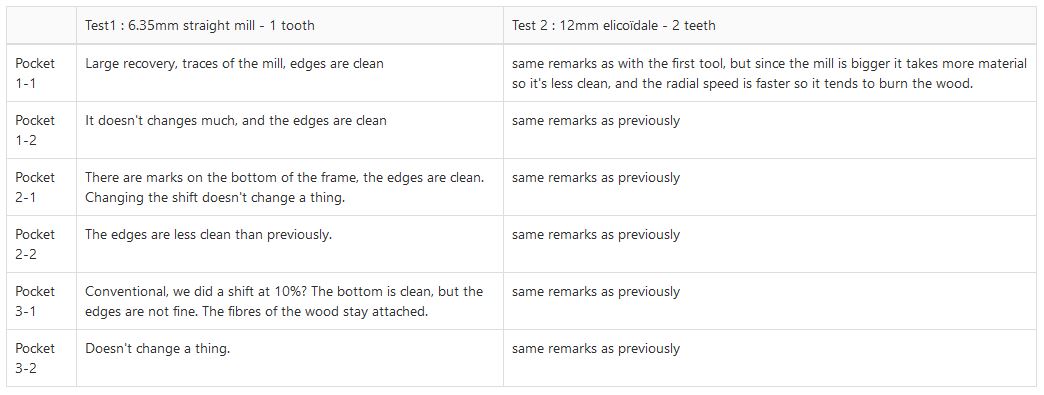
What does the type of milling tool changes in the milling process ?¶
In order to test the limitations of the machine, we did several tests with a frame of wood. Here are the results :